ISW Updates. 1/2
These are deliberately posted without comment in order for members to reach their own conclusions.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment
November 9, 9:15 pm ET
Full article: Institute for the Study of War
The pdf can be downloaded here.
Main Points.
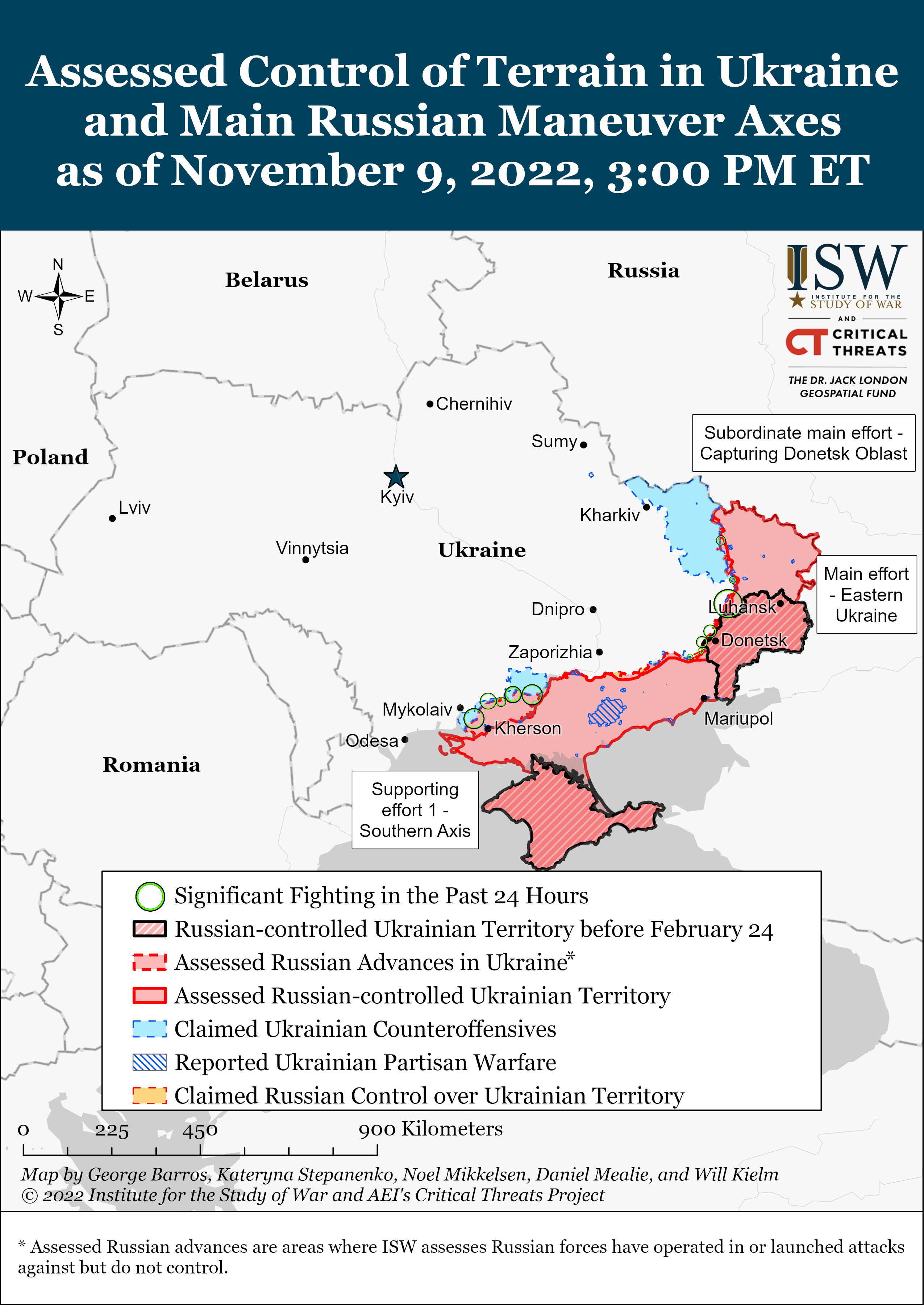
Click here to see ISW’s interactive map of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. This map is updated daily alongside the static maps present in this report.
The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) ordered Russian forces on the west (right) bank of the Dnipro River to begin withdrawing to the east (left) bank on November 9. Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu ordered the withdrawal of Russian troops across the Dnipro River during a highly staged televised meeting with Commander of the Russian Armed Forces in Ukraine Army General Sergey Surovikin on November 9. During the televised meeting, Surovikin recommended the withdrawal and Shoigu accepted his decision, giving Surovikin the task of ensuring the “safe transfer of personnel, weapons, and equipment” to the east (left) bank.[1] Shoigu and Surovikin’s statements mark the beginning of a steady, fighting withdrawal by Russian troops across the Dnipro to prepared positions on the east (left) bank to preserve the combat power of Russian units, including elements of the 76th and 106th Airborne Assault Divisions and 22nd Army Corps.[2] Surovikin notably stated that half of the troops withdrawn from the west bank of the Dnipro will be redeployed to other areas of Ukraine. The entire Russian contingent will take some time to withdraw across the Dnipro River and it is still unclear if Russian forces will be able to conduct the withdrawal in relatively good order under Ukrainian pressure.
The battle of Kherson is not over, but Russian forces have entered a new phase—prioritizing withdrawing their forces across the river in good order and delaying Ukrainian forces, rather than seeking to halt the Ukrainian counteroffensive entirely.
The Ukrainian counteroffensive in the Kherson direction since August—a coordinated interdiction campaign to force Russian forces to withdraw across the Dnipro without necessitating major Ukrainian ground offensives—has likely succeeded. As ISW has observed over the previous months, Ukrainian forces engaged in a purposeful and well-executed campaign to target Russian concentration areas, military assets, and logistics nodes throughout Kherson Oblast to make continued Russian positions on the west bank untenable without having to conduct large-scale and costly ground maneuvers to liberate territory.[3] Ukrainian troops launched constant attacks on bridges across the Dnipro River and targeted supply centers and ammunition depots on the east bank of the Dnipro that degraded the ability of Russian forces to supply the grouping on the west bank; Ukrainian forces combined these strikes with prudent and successful ground attacks on key locations such as Davydiv Brid. This campaign has come to fruition. Surovikin directly acknowledged that Russian forces cannot supply their grouping in Kherson City and the surrounding areas due to Ukrainian strikes on critical Russian supply lines to the west bank.[4] Russian sources noted that the withdrawal is a natural consequence of targeted and systematic Ukrainian strikes that cost the Russian grouping on the west bank its major supply arteries, which gradually attritted their overall strength and capabilities.[5]
The Russian withdrawal from the west bank of the Dnipro is unlikely to be a trap meant to lure Ukrainian troops into costly combat near Kherson City, as some Ukrainian and Western sources have suggested.[6] ISW has previously observed many indicators that Russian forces, military and economic assets, and occupation elements have steadily withdrawn from the west bank across the Dnipro River, and Russian officials have been anticipating and preparing for withdrawal in a way that is incompatible with a campaign to deceive and trap Ukrainian troops.[7] Russian commanders will certainly attempt to slow Ukrainian advances to maintain an orderly withdrawal, and some forces may remain to delay Ukrainian troops in Kherson City itself—but this fighting will be a means to the end of withdrawing as many Russian units as possible in good order.
The Russian information space predictably reacted to the announcement of the withdrawal with varying degrees of ire and concern. Several Russian milbloggers emphasized that the withdrawal is the natural consequence of systematic failures within Russian military and command structures and framed the withdrawal as an inevitable result of political nuances beyond the realm of military control.[8] Russian sources also emphasized that this is a major defeat for Russian forces because they are losing territory that Russia annexed and claims as its own.[9]
However, many prominent voices in the milblogger space sided with Surovikin and lauded the decision as a necessary one, indicating that Russian leadership has learned from the information effects of the disastrous Russian withdrawal from Kharkiv Oblast in mid-September.[10] A prominent Russian milblogger that has previously stridently criticized the conduct of Russian operations stated that Surovikin “got the inheritance he got” managing operations in Kherson Oblast, and implied that Surovikin did the best he could under the circumstances, so he ultimately cannot be blamed.[11] Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin voiced his support for the withdrawal and called it the “greatest achievement” made by Surovikin due to Surovikin’s stated desire to preserve the safety of Russian troops.[12] Chechen leader Ramzan Kadyrov agreed with Prigozhin’s assessment and claimed Surovikin saved thousands of lives and is seeking more advantageous positions.[13] These responses, particularly from Kadyrov and Prigozhin, are markedly different from scathing critiques previously leveled at Commander of the Grouping of Russian forces “Center” in Ukraine Colonel General Alexander Lapin following massive Russian losses in eastern Kharkiv and northern Donetsk oblasts.[14] Surovikin has steadily established an informational cover for his decision-making and the eventual Russian withdrawal from positions in Kherson Oblast since the announcement of his appointment as theatre commander of Russian Forces in Ukraine. Surovikin stated that Russian leadership will need to make “difficult decisions” regarding Kherson Oblast as early as October 19.[15] The Kremlin and senior Russian commanders appear to have learned informational and military lessons from previous failures and will likely apply these to the presentation and conduct of this withdrawal. Russian President Vladimir Putin has not commented on the withdrawal as of this publication, suggesting that the Kremlin is framing the withdrawal as a purely military decision.
Russian National Security Council Secretary Nikolai Patrushev met with senior Iranian officials in Tehran on November 9, likely to discuss the sale of Iranian ballistic missiles to Russia and other forms of cooperation. Patrushev met with Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi and Iranian Supreme National Security Council (SNSC) Secretary Ali Shamkhani.[16] The SNSC is Iran’s highest defense and security policy body and reports directly to the supreme leader. Iranian readouts of Patrushev’s meetings largely focused on economic and political cooperation, while Russian readouts emphasized that the discussion focused on security affairs.[17] Patrushev and Shamkhani discussed “measures to counter interference by Western secret services in the two countries’ internal affairs,” according to Russia’s
TASS. Iranian officials have repeatedly accused the United States and its allies of stoking the ongoing protests throughout Iran.[18] Patrushev’s visit to Tehran notably comes amid reports that Iran is seeking Russian help with protest suppression, although it is unclear whether Patrushev discussed such cooperation.[19] Patrushev likely sought to secure additional Iranian precision munitions to replenish Russia’s dwindling stocks.